Introduction:
Tree pruning is not just about shaping trees for aesthetic purposes; it is a fundamental practice that plays a significant role in maintaining the health, structure, and longevity of trees. In this guide, we’ll delve into the art of tree pruning, exploring different techniques, understanding the importance of proper pruning, and uncovering the benefits it offers to your trees and landscape.
Why is Tree Pruning Important?
- Promotes Tree Health: Pruning removes dead, diseased, or damaged branches, reducing the risk of decay and disease spread. It also encourages the development of a strong and resilient tree structure.
- Enhances Aesthetics: Proper pruning enhances the natural form and beauty of trees, improving their overall appearance and adding value to your landscape.
- Encourages Growth: Pruning stimulates new growth and directs the growth of branches, promoting optimal tree growth and vitality.
- Increases Safety: Removing hazardous branches reduces the risk of falling limbs and enhances the safety of your property and its occupants.
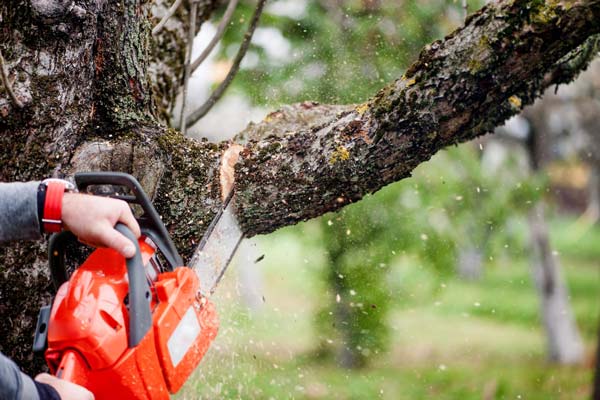
Common Pruning Techniques:
- Crown Cleaning: Removing dead, diseased, or weak branches from the canopy to improve airflow and light penetration.
- Crown Thinning: Selectively removing inner branches to reduce density and improve light penetration and air circulation throughout the canopy.
- Crown Raising: Removing lower branches to provide clearance for pedestrians, vehicles, or structures and improve visibility.
- Crown Reduction: Pruning back the outermost branches to reduce the overall size of the canopy while maintaining its natural shape.
When to Prune:
- Winter: Pruning during the dormant season (winter) is ideal for most tree species, as it minimizes stress and reduces the risk of disease transmission.
- Spring: Pruning in spring is suitable for flowering trees, as it allows for the removal of dead or damaged branches after winter.
- Summer: Light pruning can be done in summer to shape or remove small branches, but extensive pruning should be avoided to prevent stress.
- Fall: Pruning in fall is generally not recommended, as it may stimulate new growth that is susceptible to frost damage.
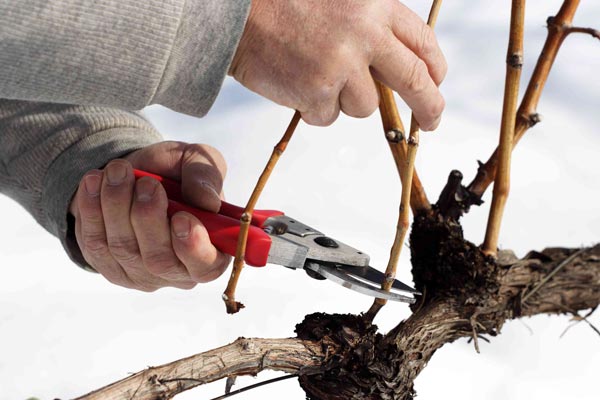
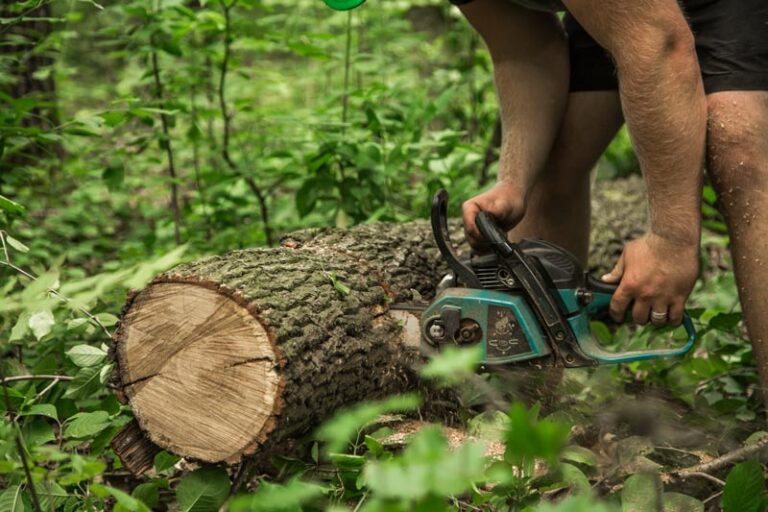
Choosing the Right Tools:
Selecting the appropriate pruning tools is essential for achieving clean and precise cuts while minimizing damage to the tree. Common pruning tools include hand pruners, loppers, pruning saws, and pole pruners, each designed for specific pruning tasks and branch sizes.
Seeking Professional Assistance:
While minor pruning tasks can be tackled by homeowners, larger or more complex pruning jobs should be entrusted to certified arborists or tree care professionals. These experts have the knowledge, experience, and equipment necessary to perform pruning safely and effectively while ensuring the long-term health and vitality of your trees.
Conclusion:
Tree pruning is both an art and a science, requiring careful consideration of tree biology, growth habits, and pruning techniques. By understanding the principles of proper pruning and incorporating it into your tree care regimen, you can promote healthier, more resilient trees and create a safer and more beautiful landscape for generations to come.